Gonavet (Canada)
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Modern Veterinary Therapeutics
Company: Modern Veterinary Therapeutics
Gonadorelin[6-D-Phe] injection
Sterile
Veterinary Use Only
DIN 02532115
Description
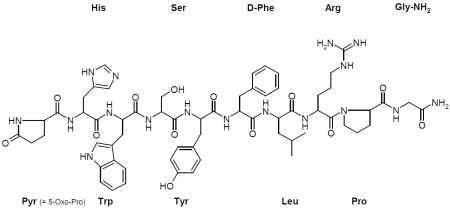
Each mL of Gonavet contains gonadorelin[6-D-Phe] acetate (equivalent to 50 µg gonadorelin[6-D-Phe]) as the active ingredient and 1 mg of chlorocresol as the preservative. Gonadorelin[6-D-Phe] is a decapeptide composed of the amino acid sequence:
5 - Oxo - L - prolyl - L - histidyl - L - tryptophyl - L - seryl - L - tyrosyl - D - phenylalanyl - L - leucyl - L - arginyl - L - prolyl - glycinamide acetate. Empirical formula is C62H81N17O13 • x CH3COOH (x = 1). Chemical structure:
Therapeutic classification:
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist
Gonavet Indications
In dairy cattle:
- Induction of ovulation
- Synchronization of estrous cycles to allow for fixed-time artificial insemination
- Treatment of ovarian cysts
Dosage and Administration
For intramuscular injection, preferably in the neck region. The product is intended for single administration except when used as part of a fixed-time artificial insemination protocol.
Dairy Cattle (IM): 100 µg Gonadorelin[6-D-Phe] (2 mL)
Warnings
No withdrawal period or milk withholding time is required for cattle when treated according to the label. Pregnant women should not administer the product and women of child-bearing age should administer the product with caution. People with known hypersensitivity to GnRH analogues should avoid handling this product. Caution should be taken to avoid accidental self-injection and contact with skin and eyes. In case of accidental self-injection, seek medical advice immediately and show the label to the physician. In case of accidental skin or eye contact, rinse immediately with water. Keep out of reach of children.
Contraindications
Do not use in cows with a mature tertiary follicle ready to ovulate.
Do not use during infectious diseases and other relevant health disorders.
Do not use in case of known hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Cautions:
To maximize conception rates of cows to be treated with GnRH-PGF based synchronization protocols, the ovarian status should be determined and regular cyclic ovarian activity confirmed. Optimal results will be achieved in healthy normally cycling cows.
Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamic properties:
Gonadorelin[6-D-Phe] is an agonist of the natural GnRH formed in the hypothalamus that is excreted in a pulsatile manner into the pituitary portal vein circulation and controls the synthesis of the follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinising hormone (LH) in the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland, as well as, LH secretion. The pulse frequency and amplitude of the GnRH excretion are dependent on the stage of the estrous cycle. Along with FSH, LH stimulates the release of estrogen from maturing follicles in the ovaries and induces ovulation. Gonadorelin[6-D-Phe] acetate has the same effect as endogenous GnRH: the LH peak in the spontaneous cycle is imitated and causes follicular maturation and ovulation or stimulates a new follicle maturation wave. With high dosage, repeated or continuous application of an agonist, the gonadotropic cells in the pituitary become temporarily refractory.
Pharmacokinetic particulars:
Following parenteral administration, GnRH and its analogues are absorbed rapidly and are distributed and eliminated from the organism following one-compartment-model kinetics. The plasma half-life is a few minutes (natural GnRH) up to 2 hours. The biological half-life of the natural, as well as the synthetic agonists, is short. Break-down occurs by enzymes in the form of peptidases and the excretion is primarily renal. The degradation products have no hormonal activity.
Gonadorelin[6-D-Phe] is a linear decapeptide that can only be differentiated due to the difference in the amino acid at position 6 of GnRH: instead of glycine in natural GnRH, Gonadorelin[6-D-Phe] contains D-phenylalanine. This modification leads to a higher resistance against the catabolising enzymes.
Efficacy:
Synchronization of estrus cycles:
266 anestrus dairy cows of second lactation and over, with no signs of heat until 60 days post-partum were administered Gonavet 100 μg on day 60 postpartum, 500 µg PGF2α 7 days later, and Gonavet 100 µg 24 - 30 hours after prostaglandin administration. The first artificial insemination (AI#1) was carried out 16 - 24 hours after the second administration of Gonavet. All 266 animals demonstrated estrous. Sixty-one percent (163/266) became pregnant after AI#1, 18 of them were in heat again after 6 - 9 weeks.
Induction of ovulation:
A series of four trials conducted in Germany assessed the effect of Gonavet on ovulation induction in dairy cattle. The first study included 297 cows from two farms. Enrolled cows had at least one unsuccessful insemination. At the time of spontaneous estrus and prior to insemination, cows were either treated with 100 μg Gonavet or were left untreated. Seventy-four (74) percent of treated cows had an ovulation vs. 56% in untreated. The proportion of animals with delayed ovulation (F4 > 24 h. post AI) was reduced in the treated group (26% vs. 44%). A second trial was conducted on 253 cows treated with 100 µg Gonavet and 245 untreated animals from five farms. The difference in the ovulation rate between the treatment and the control group was statistically significant (83% with Gonavet vs. 75%). A third trial was conducted in 230 cows treated with 100 µg Gonavet and 213 untreated animals from five farms. There was a significant reduction of the proportion of animals with delayed ovulation following treatment with Gonavet in comparison to controls (52% vs. 57%). A fourth trial with 935 experimental and 911 untreated animals from 12 farms was conducted. The ovulation rate was increased by 10% in 11 out of 12 farms with Gonavet.
Ovarian cysts:
A study was conducted to investigate the effect of the GnRH analogue (D-Phe6-GnRH) on Ovarian cysts in dairy cattle in doses of 50 µg or 100 µg compared to a control group. The D-Phe6-GnRH analogue confirmed its adequacy for the treatment of ovarian cysts in cattle after IM administration. The efficacy of the 100 µg dosage was confirmed. No adverse events were observed in either treatment group after IM application of the D-Phe6-GnRH analogue.
Storage
Store between 2°C - 8°C. Keep the vial in the original carton in order to protect from light. Once broached, product may be stored at temperatures up to 25°C. Shelf life after first opening the immediate packaging: 28 days.
Presentation:
Gonavet is available in 20 mL and 50 mL multi-dose vials.
Manufactured for:
Modern Veterinary Therapeutics, LLC, Miami, Florida 33186 - USA
Tel. +1 888 590 9839
Fax +1 305 503 8585
info@modernveterinarytherapeutics.com
www.modernveterinarytherapeutics.com
Imported by:
Modern Veterinary Therapeutics Inc., 261065 Wagon Wheel Way, Bay 3, Balzac (Rocky View County), AB T4A 0T5
Orders & Product information: Call 1 888 590 9839
Made in The Netherlands.
Revision Date: 14 Oct 2022
V03.22 (CA) Mus
CPN: 1354032.0
261065 WAGON WHEEL WAY, ROCKY VIEW COUNTY, AB, T4A 0T5
| Telephone: | 407-852-8039 | |
| Toll-Free: | 888-590-9839 | |
| Website: | www.modernveterinarytherapeutics.com | |
| Email: | info@modernveterinarytherapeutics.com |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". Animalytix assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the Animalytix service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2024 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2024-02-27
